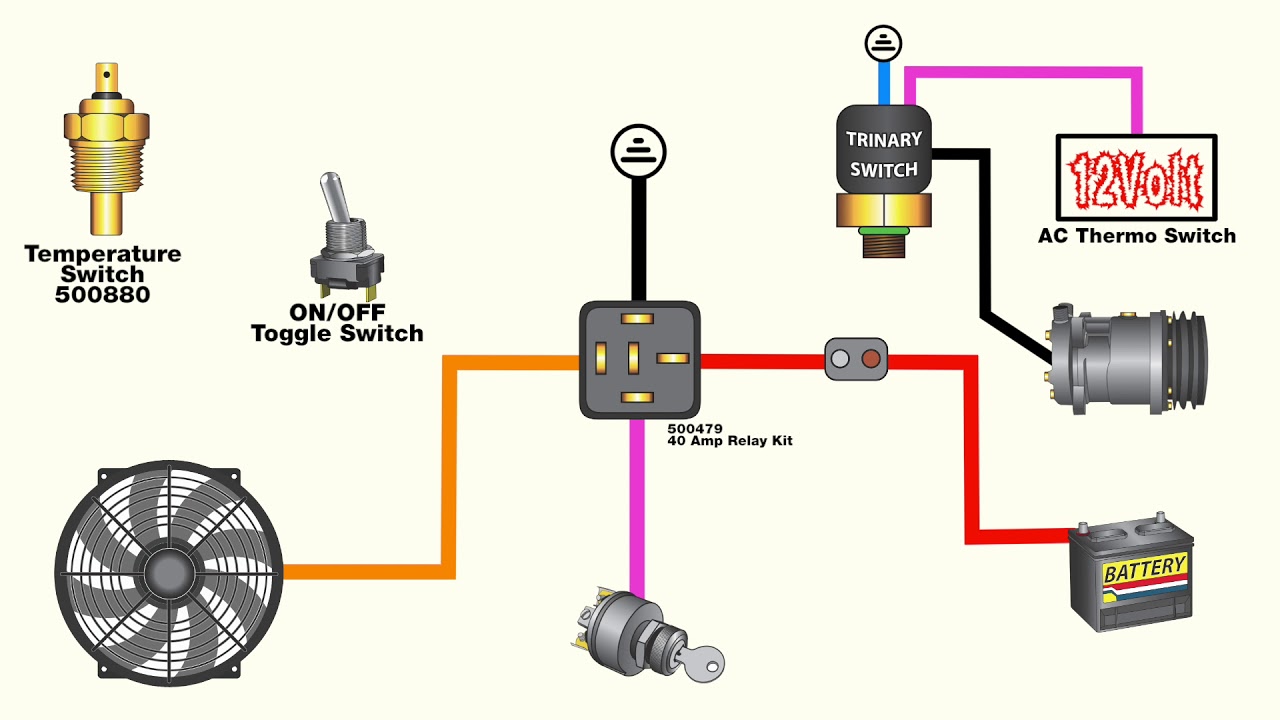
Revolutionizing Engine Cooling: The Auto Relay Switch for Cooling Fans

Overheating: the bane of any internal combustion engine. It can lead to catastrophic failures, costly repairs, and frustrating downtime. But what if there was a simple, automated solution to keep your engine running cool? Enter the unsung hero of thermal management: the auto relay switch for cooling fans.
The automatic relay switch is a small but mighty component that regulates the operation of your vehicle's cooling fan. Unlike older, manually switched systems, these smart relays automatically activate the fan when the engine reaches a predetermined temperature, ensuring optimal cooling without constant driver intervention. This seemingly simple function has revolutionized engine cooling, leading to improved performance, fuel efficiency, and engine longevity.
Before automatic cooling fan relays, vehicles relied on mechanical fan clutches or switches activated by the driver. These older methods were less efficient, often leading to either excessive fan operation, wasting power, or insufficient cooling, risking overheating. The advent of the automatic relay, leveraging temperature sensors and electronic controls, brought a new era of precision and efficiency to engine cooling.
The core function of a cooling fan automatic relay switch is to act as an intermediary between the vehicle's electrical system and the cooling fan motor. The relay receives a signal from a temperature sensor, typically located in the coolant or engine block. When the sensor detects that the engine temperature has reached a preset threshold, it triggers the relay, which then closes a circuit, allowing power to flow to the cooling fan motor. This automated process ensures the fan only operates when necessary, optimizing both cooling performance and energy consumption.
Issues can arise with these relays, ranging from faulty sensors to corroded connections. A malfunctioning relay can lead to the fan running constantly, draining the battery, or failing to activate when needed, causing the engine to overheat. Understanding the function and potential problems associated with these relays is crucial for maintaining a healthy engine.
An automatic cooling fan relay switch essentially acts as an automated on/off switch for your vehicle's cooling fan. Think of it as a thermostat for your engine's cooling system. When the engine gets too hot, the "thermostat" (temperature sensor) tells the "switch" (relay) to turn on the "air conditioner" (cooling fan). This simple analogy highlights the crucial role of the relay in maintaining optimal engine temperature.
Benefits of using an automatic cooling fan relay include improved fuel efficiency due to reduced fan operation, extended engine life by preventing overheating, and enhanced overall vehicle performance.
Installing a new automatic cooling fan relay usually involves locating the existing relay, disconnecting the wiring, and installing the new relay in its place. Always refer to your vehicle's service manual for specific instructions.
Here's a simple checklist for troubleshooting a potentially faulty cooling fan relay:
1. Check the fuse.
2. Inspect the relay for physical damage.
3. Test the relay with a multimeter.
4. Verify the temperature sensor is functioning correctly.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Auto Relay Switch for Cooling Fan
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved Fuel Efficiency | Potential Relay Failure |
| Extended Engine Life | Sensor Malfunction can affect operation |
| Automated Cooling Management | Wiring Issues can cause problems |
Five best practices for implementing an automatic cooling fan relay switch include using high-quality relays, ensuring proper wiring connections, selecting the correct temperature rating for the relay, regularly inspecting the relay for signs of wear and tear, and consulting a qualified mechanic if you are unsure about any aspect of the installation or troubleshooting process.
Five real-world examples of vehicles utilizing automatic cooling fan relays include most modern cars, trucks, SUVs, motorcycles, and even some off-road vehicles.
Challenges related to automatic cooling fan relays include relay failure, sensor malfunction, wiring problems, improper installation, and incorrect temperature ratings. Solutions involve replacing faulty components, ensuring correct wiring, proper installation procedures, and selecting the correct relay for your vehicle.
FAQs:
1. What is an auto relay switch? A: An electrical switch that controls the cooling fan operation.
2. How does it work? A: It activates the fan based on engine temperature.
3. Why is it important? A: Prevents overheating and improves efficiency.
4. What are the signs of a bad relay? A: Overheating or fan not running.
5. How do I replace it? A: Consult your vehicle's service manual.
6. How much does a relay cost? A: Typically between $10 and $30.
7. Where can I buy one? A: Auto parts stores or online retailers.
8. Can I install it myself? A: Yes, with basic mechanical skills.
Tips and tricks include using dielectric grease on connections to prevent corrosion and checking the fuse before replacing the relay.
In conclusion, the auto relay switch for cooling fans has become a vital component in modern vehicles. It plays a critical role in maintaining optimal engine temperature, improving fuel efficiency, and extending engine life. Understanding its function, benefits, and potential issues empowers vehicle owners to ensure their cooling systems operate efficiently and reliably. From preventing overheating to maximizing performance, the automatic relay is a small component with a big impact. By following best practices and understanding troubleshooting steps, drivers can ensure their engines stay cool and perform at their best. Don't underestimate the importance of this small but powerful component – it could save you from costly repairs and frustrating breakdowns. Take the time to understand your vehicle's cooling system and the essential role of the automatic relay switch.
Dominate week 8 unlocking the top fantasy football defenses
The intrigue of demon skull tattoo designs
Festive simple 4th of july nail art ideas