Navigating the Labyrinth: Federal Job Classification
So, you're thinking about a federal government job? Power moves, huh? Forget the corner office with a view – think cubicle chic and the potential to shape policy. But before you start envisioning yourself briefing the President, you need to understand the federal government's intricate system of job classification – the infamous General Schedule (GS) system and its associated levels, commonly referred to as federal steps and grades.
This system, a labyrinthine structure of numbered grades and steps, determines everything from your starting salary to your potential for career advancement. It's the framework that dictates your place in the federal hierarchy, and navigating it can feel like deciphering ancient hieroglyphics. Don't worry, we're here to decode the jargon and help you understand how these federal classifications really work.
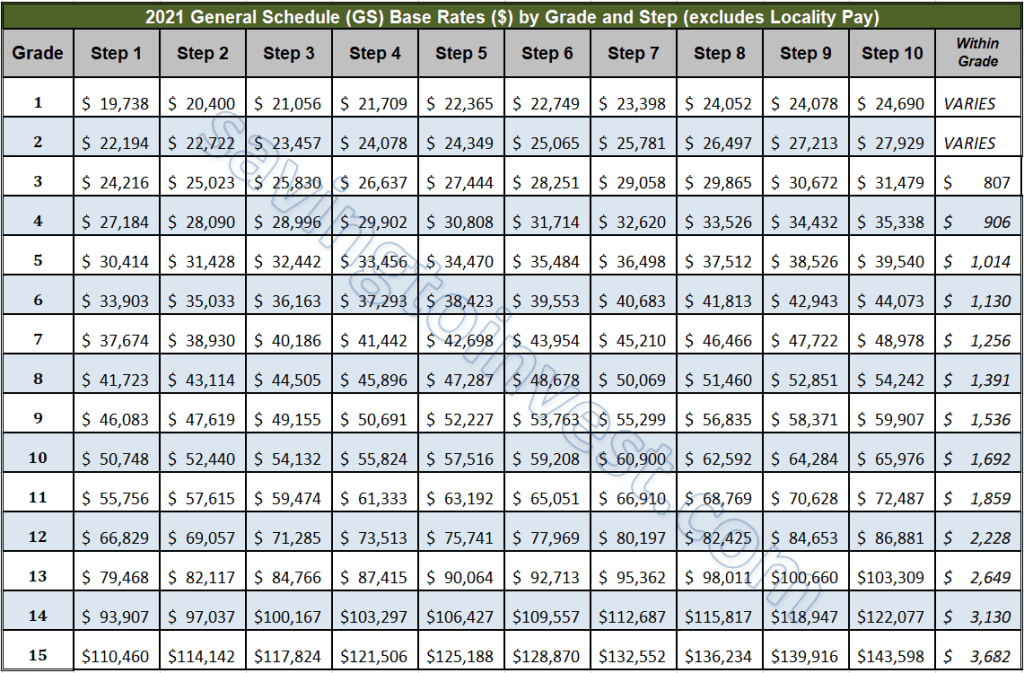
The GS system is essentially a standardized way of categorizing and paying federal employees. Each job is assigned a GS level, ranging from GS-1 (entry-level) to GS-15 (senior executive). Within each grade, there are 10 steps, representing incremental salary increases based on time in service and performance. These steps within the grade are the "federal steps" we're talking about. Think of it like climbing a ladder – each grade is a different rung, and each step is a little boost upward within that rung.
But why this complex system? Historically, the GS system was created to standardize pay and promote fairness within the federal workforce. Before its implementation, federal salaries were often arbitrary and prone to political influence. The GS system aimed to establish a more merit-based system tied to job responsibilities and experience. Over time, it has evolved, becoming more intricate while still aiming to provide structure and transparency in federal employment.
Understanding the nuances of federal steps and grades is crucial for anyone considering or currently employed by the federal government. Your GS grade and step determine not only your salary but also your eligibility for certain positions and promotions. Moving up the ladder – advancing in grade and step – is essential for career progression and earning potential. This seemingly bureaucratic structure holds the key to unlocking your federal career ambitions.
One of the primary benefits of this structured approach is the transparency it provides. Employees know exactly where they stand and what the requirements are for advancement. Another advantage is the standardization across different agencies and departments. A GS-9 position at the Department of Defense, for example, will have similar responsibilities and pay as a GS-9 position at the Department of Justice. This ensures consistency and fairness in compensation across the federal workforce. Finally, the step increases within a grade offer a clear path for salary growth based on experience and satisfactory performance.
Successfully navigating the federal steps and grades involves understanding your position description, performance expectations, and the promotion criteria. Regularly review your agency’s promotion policies and seek feedback from supervisors to ensure you're meeting the requirements for advancement. Actively participating in training and development programs can also enhance your qualifications and increase your chances of promotion. One example is a GS-7 employee consistently exceeding performance expectations and receiving positive feedback from supervisors, leading to promotion to GS-9 within two years.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS System
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Transparency and Standardization | Rigidity and Bureaucracy |
| Clear Path for Advancement | Limited Flexibility in Compensation |
| Fair and Equitable Compensation | Can Discourage Innovation and Risk-Taking |
Best Practices for Navigating Federal Steps and Grades:
1. Understand Your Position Description: Thoroughly review your PD to understand the responsibilities and requirements.
2. Seek Regular Feedback: Actively seek feedback from supervisors to identify areas for improvement and ensure you're meeting expectations.
3. Document Your Accomplishments: Keep a detailed record of your achievements and contributions to demonstrate your value.
4. Network and Build Relationships: Build professional relationships within your agency and across the federal government.
5. Pursue Professional Development: Take advantage of training opportunities to enhance your skills and knowledge.Frequently Asked Questions about Federal Steps and Grades:
1. What is a GS level? (Answer: A grade within the General Schedule system.)
2. How many steps are in each grade? (Answer: Typically 10.)
3. How do I get promoted to the next grade? (Answer: By meeting performance requirements, time-in-grade requirements, and competing for open positions.)
4. What is a within-grade increase? (Answer: A step increase within the same grade based on time and performance.)
5. Can I negotiate my salary? (Answer: Generally, no. Salaries are set by the GS system.)
6. What is a special rate table? (Answer: A pay table used for certain occupations in high-demand locations.)
7. How can I find out more about federal job classifications? (Answer: The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) website is a great resource.)
8. What are some tips for advancing my federal career? (Answer: Seek mentorship, network, and pursue professional development opportunities.)In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of the federal steps and grades, commonly referred to as the General Schedule (GS) system, is essential for anyone seeking a career in the federal government. While the system may seem complex, it offers a structured and transparent pathway for career progression. By understanding the nuances of grades, steps, and promotion criteria, individuals can effectively navigate the system, advance their careers, and achieve their professional goals within the federal workforce. It is crucial to remember that the GS system is designed to ensure fairness and consistency in compensation and promotions across the vast federal government landscape. Take the time to research, understand the system, and actively manage your career within its framework. Your future self will thank you.
Unlocking style with home depot gray paint
Unlocking savings your guide to paperstyle free shipping codes
Decoding law ping man dermato a comprehensive guide