Navigating the GS-15 Step 10 Salary Landscape

Within the intricate tapestry of federal employment, the GS-15 Step 10 pay grade represents a pinnacle of achievement, a summit of professional ascent. It signifies years of dedicated service, specialized expertise, and a significant contribution to the public sector. But like any summit, reaching this height requires understanding the terrain, navigating the complexities, and appreciating the view from the top.
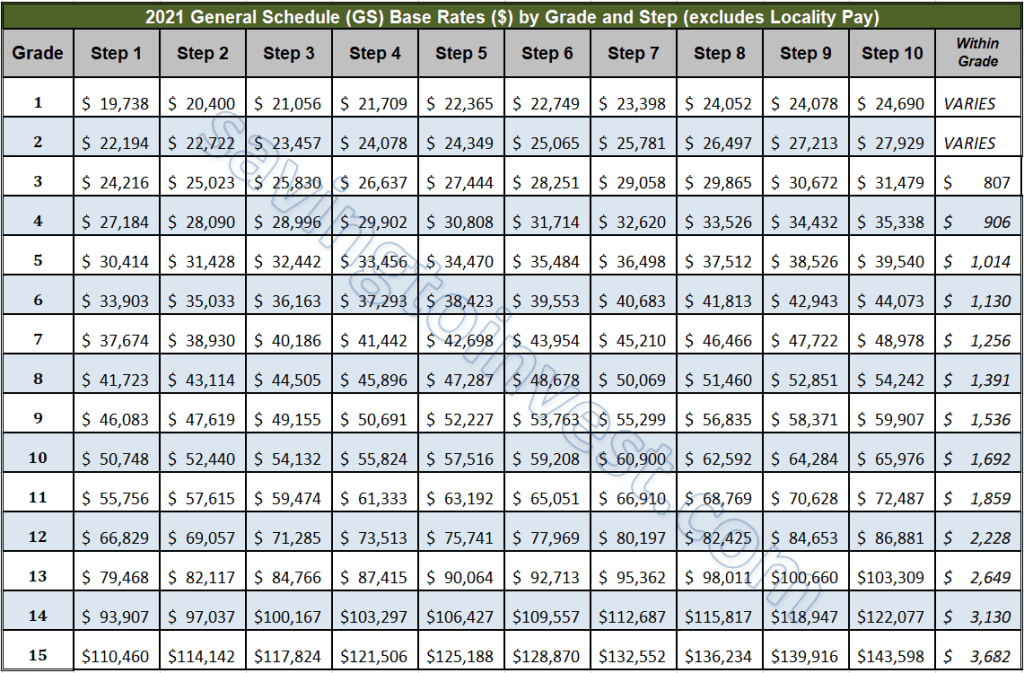
What does it mean to reach GS-15 Step 10? This question resonates with ambition, financial security, and the culmination of a career trajectory. For many federal employees, this level represents the highest achievable rung on the General Schedule (GS) payscale ladder. It is a point where salary progression within the grade plateaus, bounded by the GS-15 Step 10 pay cap. Understanding this upper limit is crucial for long-term financial planning and career management.
The history of the GS pay system is interwoven with the evolution of the federal workforce. Established to standardize compensation and promote fairness, the GS system has undergone numerous revisions over the decades. The concept of a pay cap for higher grades, like GS-15 Step 10, emerged as a mechanism for managing budgetary constraints while still rewarding experience and expertise. This cap, while sometimes a source of frustration for those who reach it, plays a role in the overall balance of the federal compensation structure.
The implications of the GS-15 Step 10 salary ceiling are far-reaching, impacting not only individual employees but also the dynamics of the federal workforce. It can influence recruitment and retention, especially for highly specialized roles where private sector salaries might offer greater earning potential. Understanding these implications is essential for policymakers and federal agencies striving to attract and retain top talent.
Navigating the complexities of the GS-15 Step 10 pay cap requires a nuanced perspective. It necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the federal pay system, retirement benefits, and other factors that contribute to overall financial well-being. This understanding empowers employees to make informed decisions about their careers and financial futures.
The GS-15 Step 10 pay cap represents the maximum base salary for an employee at this level. It's important to differentiate between base salary and total compensation, which can include locality pay adjustments, bonuses, and other benefits. For example, an employee in a high-cost-of-living area may receive a locality pay adjustment that significantly increases their overall earnings, even though their base salary is capped at the GS-15 Step 10 level.
While the GS-15 Step 10 pay cap limits further base salary increases within the grade, it doesn't necessarily signify the end of professional growth. Opportunities for career advancement may still exist through promotions to Senior Executive Service (SES) positions or other leadership roles, which often come with higher salary potential.
One benefit of reaching GS-15 Step 10 is the stability and predictability it offers for financial planning. Knowing the upper limit of base salary allows for long-term budgeting and investment strategies.
Another potential benefit is the increased focus on non-monetary rewards. Reaching the pay cap may encourage employees to prioritize professional development, mentorship, or other forms of job satisfaction that extend beyond financial compensation.
Finally, the achievement of GS-15 Step 10 can be a significant source of personal and professional pride, representing the culmination of years of hard work and dedication.
Advantages and Disadvantages of GS-15 Step 10 Pay Cap
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Predictable Salary | Limited Earning Potential within the Grade |
| Focus on Non-Monetary Rewards | Potential for Reduced Motivation in Some Cases |
| Sense of Accomplishment | Challenges in Attracting Top Talent in Competitive Fields |
Frequently Asked Questions about GS-15 Step 10 Pay Cap:
1. What is the current GS-15 Step 10 salary? (Answer: This varies based on locality pay adjustments. Consult the OPM website for the most up-to-date information.)
2. How long does it typically take to reach GS-15 Step 10? (Answer: This depends on individual career progression and agency promotion policies.)
3. Are there opportunities for salary increases beyond GS-15 Step 10? (Answer: Yes, through promotions to SES positions or other leadership roles.)
4. How does the pay cap impact retirement calculations? (Answer: Retirement benefits are calculated based on the "high-3" average salary, which can include locality pay adjustments.)
5. What are the implications of the pay cap for employee retention? (Answer: The cap can influence retention, especially in high-demand fields where private sector salaries are competitive.)
6. How can I plan for my financial future after reaching GS-15 Step 10? (Answer: Consult with a financial advisor and consider long-term investment strategies.)
7. Are there resources available to help me understand the federal pay system? (Answer: Yes, the OPM website provides comprehensive information on federal pay and benefits.)
8. What are some strategies for navigating the complexities of the GS-15 Step 10 pay cap? (Answer: Understand your total compensation package, explore opportunities for professional development, and seek guidance from mentors or career advisors.)
In conclusion, the GS-15 Step 10 pay cap represents a significant milestone in a federal employee's career. While it signifies the maximum base salary within the GS-15 grade, it doesn't necessarily mark the end of professional growth or financial advancement. By understanding the nuances of the federal pay system, exploring alternative avenues for career progression, and focusing on the broader aspects of job satisfaction, employees can effectively navigate the complexities of the GS-15 Step 10 landscape and continue to thrive in their chosen field. This requires careful planning, a deep understanding of the regulations, and a proactive approach to career management. Embracing lifelong learning, seeking mentorship, and staying informed about changes in federal compensation policies are crucial steps for achieving long-term success and maximizing one's overall financial well-being. It's vital to remember that career fulfillment encompasses more than just monetary compensation, and reaching GS-15 Step 10 can open doors to new opportunities for leadership, influence, and meaningful contribution to public service.
Unlocking agreeable gray the ultimate guide to complementary decor colors
Elevate your eportfolio mastering aesthetic backgrounds
Decoding bike wheel sizes your ultimate guide