Decoding the Matrix: Understanding Wage Grade Advancements
Ever wondered how your salary climbs the ladder? It's not magic, it's often mapped out in a system – a framework some call a wage grade increase chart, a salary progression matrix, or a compensation growth plan. These charts are the backbone of fair and transparent compensation systems, outlining how employees can advance financially within an organization.
These structured salary progression guidelines are more than just numbers on a spreadsheet. They represent a crucial link between performance, experience, and reward. Understanding these structures empowers employees to navigate their career paths strategically, setting clear expectations and fostering motivation. For organizations, they offer a structured approach to managing compensation, ensuring equity and promoting a culture of growth.
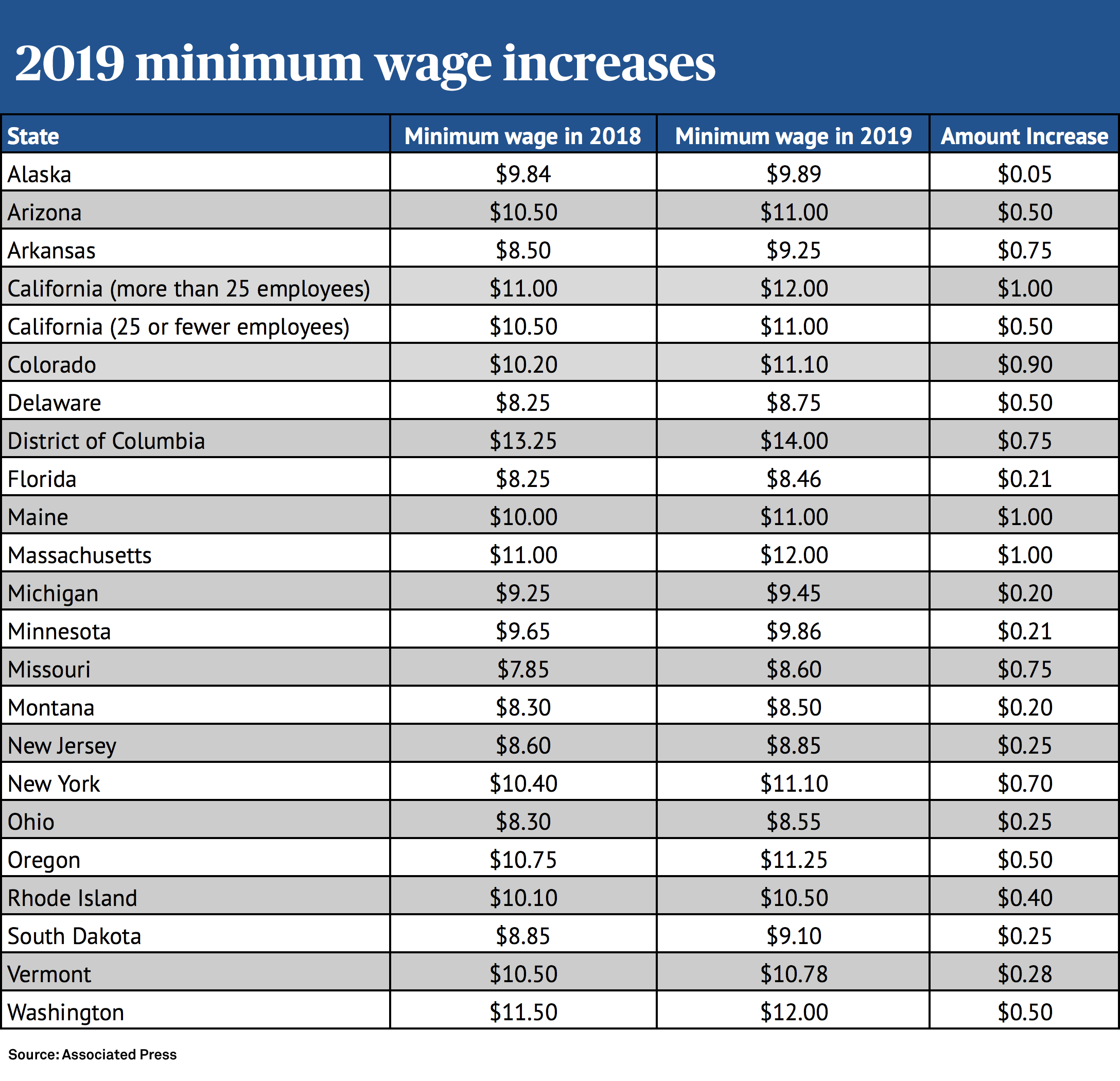
The historical roots of formalized pay structures lie in the industrial era, evolving alongside the rise of large organizations and the need for standardized compensation systems. Initially, these systems were often simple, based primarily on tenure. Over time, they’ve become increasingly sophisticated, incorporating factors like performance, skill development, and market competitiveness.
Wage grade systems play a vital role in addressing pay equity concerns. By establishing clear criteria for salary increases, they mitigate the risk of bias and promote fairness. These charts can be powerful tools for transparency, helping employees understand how their compensation is determined and what they need to achieve to progress.
However, implementing and managing these systems isn’t without its complexities. Issues can arise from outdated charts that don't reflect current market rates, poorly defined performance metrics, or a lack of communication about how the system operates. These challenges underscore the importance of regularly reviewing and updating wage grade structures to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
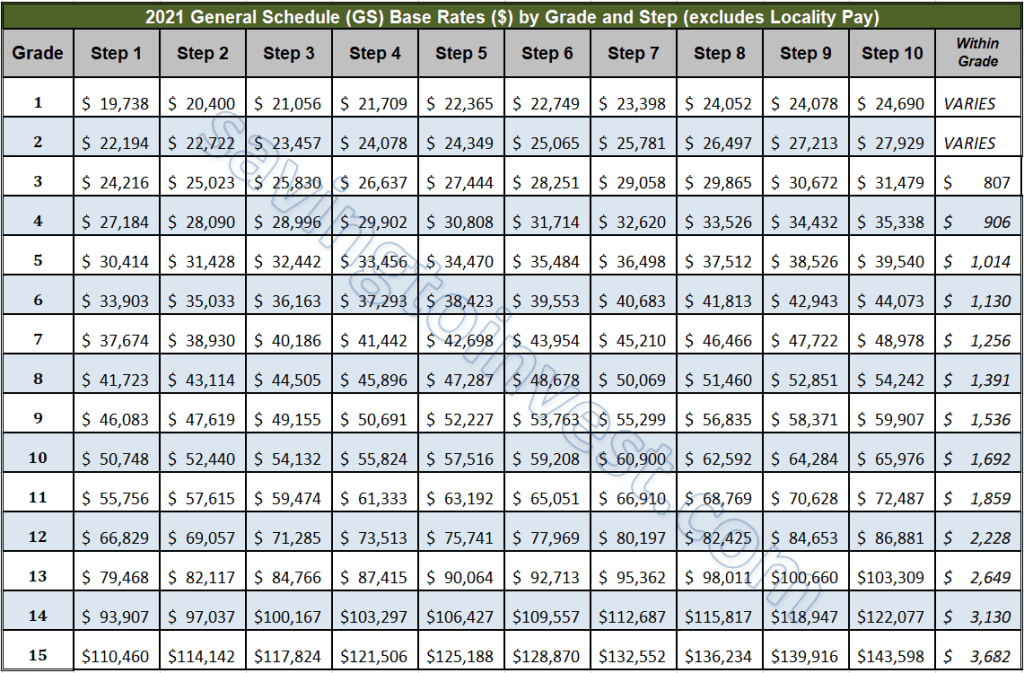
A typical wage grade increase chart lays out different pay grades or levels, each associated with a salary range. Movement between grades often depends on factors like performance reviews, skill acquisition, or promotions. For example, an entry-level employee might start at Grade 1, with potential to move to Grade 2 after demonstrating proficiency and meeting specific performance goals.
Benefits of well-implemented wage grade systems include increased employee motivation, improved retention rates, and enhanced organizational transparency. When employees see a clear path for financial growth, they’re more likely to be engaged and committed to their roles. This, in turn, can reduce costly employee turnover.
Creating an effective wage grade structure requires careful planning. Begin by analyzing market data to establish competitive salary ranges for different roles and levels. Then, define clear performance metrics that align with organizational goals. Communicate the structure clearly to all employees, ensuring they understand how the system works and how it benefits them.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wage Grade Increase Charts
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Transparency and Clarity | Potential Rigidity |
| Improved Employee Motivation | Administrative Burden |
| Enhanced Retention | Difficulty Keeping Up with Market Fluctuations |
Five best practices for implementation include: regular market analysis, clear performance metrics, transparent communication, flexibility for exceptional performance, and periodic reviews of the system.
Real-world examples are numerous. Government agencies often utilize detailed wage grade systems, as do large corporations with clearly defined job hierarchies. For instance, a software engineer might progress through different grades as they gain experience and expertise.
Challenges can include keeping up with market rate changes and managing employee expectations. Solutions involve regular reviews and adjustments to the system, coupled with open communication.
FAQs: How often are charts updated? What factors influence grade progression? How are performance metrics determined? How is market data incorporated? How are discrepancies addressed? Can employees negotiate salaries? What happens during promotions? How does this affect benefits?
Tips: Understand your company’s system. Track your progress. Seek feedback. Communicate your goals.
In conclusion, wage grade increase charts, salary progression matrices, and other compensation growth plans are integral to modern workplace dynamics. They offer a roadmap for financial advancement, promoting transparency and motivating employees. While implementing and managing these systems requires careful planning and execution, the benefits of increased employee engagement, improved retention, and a more equitable compensation structure make the effort worthwhile. Understanding and utilizing these tools effectively can significantly impact career trajectories and organizational success. Take the time to understand your company's system, ask questions, and actively manage your career growth within its framework. Your future self will thank you for it.
Iconic musical individuals a journey through the greatest solo artists
Apple account recovery time a comprehensive guide
Unlocking the power of benjamin moore black matte paint